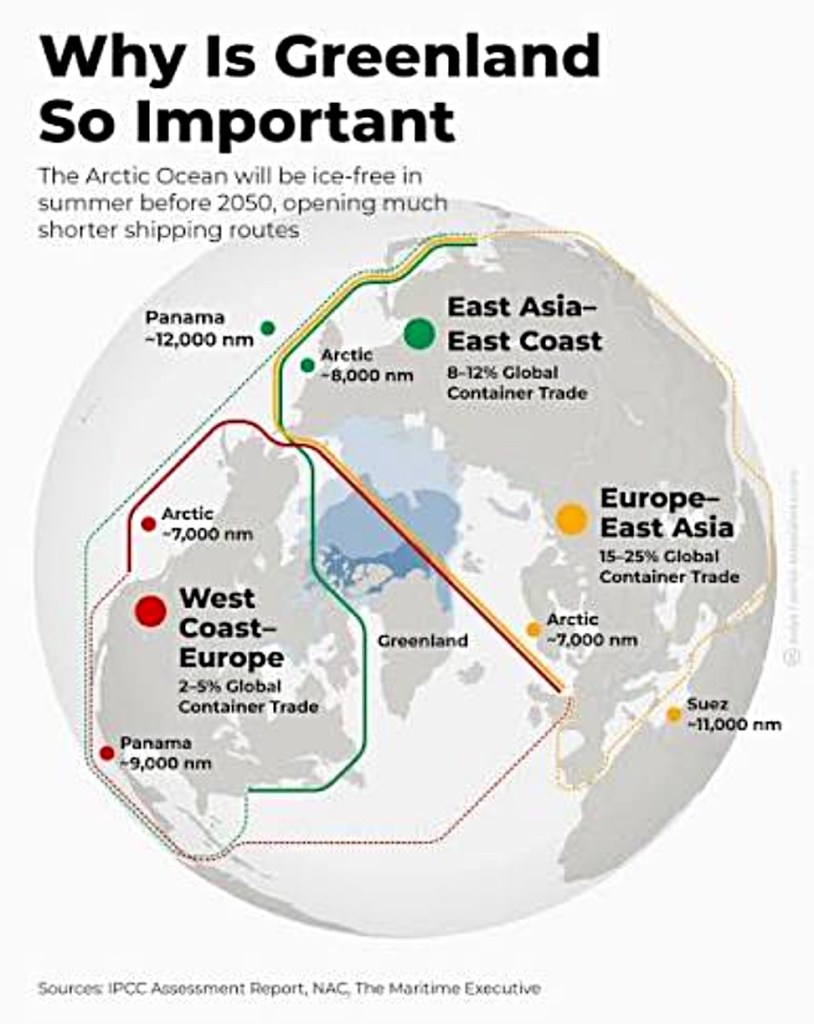
Introduction
By 2040, Europe remains a politically and militarily fragmented continent. Despite holding one of the largest combined economies globally, the lack of a fully federated European model constrains its ability to project independent military power. While selective nations—France, Germany, and the United Kingdom—maintain significant capabilities, structural fragmentation, divergent national priorities, and complex governance systems limit Europe’s strategic autonomy. This essay examines the interplay of structural, economic, and political factors that define Europe’s military posture in 2040, assessing both its achievements and persistent limitations.
Fragmented Military Capabilities
Europe’s military architecture remains characterized by a multiplicity of national forces operating independently. France continues to maintain its nuclear triad and expeditionary capability, Germany fields technologically advanced armored and air units, and Italy projects regional influence in the Mediterranean. Other nations, such as Poland, Sweden, and Spain, contribute niche capabilities, particularly in cyber operations, rapid reaction forces, and intelligence. Smaller states provide specialized units, maritime patrol, or logistics support, creating a patchwork network of competencies rather than a unified force.

Coordination among these forces relies heavily on NATO and EU initiatives, such as PESCO and the European Defence Fund. While these programs enable some joint projects—like the Franco-German Main Ground Combat System or European satellite constellations—they remain voluntary, unevenly funded, and constrained by national political approval processes. Interoperability challenges persist. Differences in equipment, standards, and doctrines limit joint deployments, and multinational exercises rarely achieve the cohesion seen in fully unified forces like the U.S. military. Duplication of expensive programs—such as fifth-generation fighter jets, armored vehicles, and naval platforms—absorbs resources that could otherwise be used for operational readiness or strategic reach.
Reliance on Alliances
By 2040, Europe’s military security remains deeply intertwined with NATO, and by extension, the United States. U.S. nuclear and conventional capabilities continue to provide the ultimate deterrent, filling the strategic gaps that fragmented European forces cannot address independently. Europe has developed limited rapid-reaction forces, capable of responding to crises in Eastern Europe or North Africa. Yet sustained expeditionary operations beyond the continent’s periphery remain rare, and the logistical complexity of multinational operations constrains Europe’s ability to project power unilaterally.
The reliance on alliances introduces both opportunities and vulnerabilities. While NATO provides shared capabilities, it reinforces a strategic dependence that limits Europe’s ability to act independently, particularly in regions where U.S. interests diverge from European priorities. Additionally, coordination across multiple nations slows decision-making, delaying responses in rapidly evolving crises.
Political and Social Constraints
Europe’s military fragmentation reflects deep-seated political and social realities. National governments prioritize sovereignty, historical sensitivities, and domestic public opinion over centralized military integration. France maintains a strong independent nuclear posture, but attempts to build multinational European forces are constrained by reluctance among smaller states to cede influence. Germany, constrained by post-World War II norms and public skepticism about military engagements, limits its willingness to commit forces beyond NATO obligations. Smaller EU nations often prefer reliance on U.S. security guarantees rather than costly investments in expeditionary capabilities.
Demographic trends exacerbate these challenges. Aging populations across much of Western Europe reduce the pool of active-duty personnel, forcing militaries to rely increasingly on technology, automation, and private contractors. Recruitment shortfalls in countries like Italy, Spain, and Greece create gaps in capability, while wealthier states such as France and Germany struggle to integrate conscript-aged populations into modern, technologically advanced forces. Social constraints—such as skepticism about European military engagement—also influence political willingness to commit forces to conflicts outside Europe.
Technological and Strategic Achievements
Despite structural limitations, Europe in 2040 has achieved selective strategic successes. Investments in high-tech military domains—cyber defense, satellite-based intelligence, precision-guided long-range weapons, and autonomous systems—allow certain nations to exert disproportionate influence relative to conventional troop numbers. French and German space-based reconnaissance and missile capabilities, for example, provide leverage in regional security operations, particularly in Africa and Eastern Europe. Similarly, European cyber defense networks, though fragmented, are capable of coordinated responses to hybrid threats and disinformation campaigns.
Regional interventions have become more effective through voluntary coalition formations. French-led operations in North Africa and combined European deployments in Eastern Europe demonstrate the potential of pooled capabilities, even in the absence of federalized command structures. Nevertheless, these interventions remain short-term and limited in scale, reflecting political caution and resource constraints.
Europe in 2040 demonstrates the limits of military power without political federation. While individual nations retain significant capabilities, and regional coalition efforts allow for selective influence, fragmentation, political caution, and logistical inefficiency prevent Europe from achieving true global strategic autonomy. Economic wealth and technological sophistication partially offset these limitations, but Europe remains a secondary global military actor, capable of defending its interests and projecting influence regionally, but dependent on alliances for comprehensive global security. The trajectory suggests that without deeper political and military integration, Europe will remain influential but constrained, unable to rival the global reach of the United States or China.